PTEN
PTEN
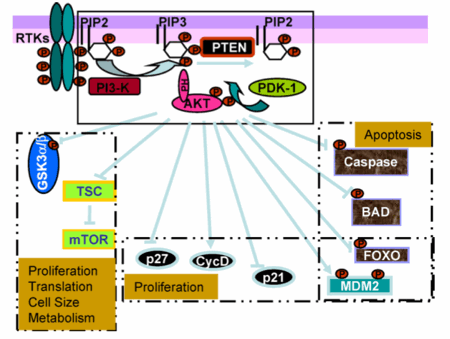
PTEN is a lipid phosphatase that negatively regulates the PI3K signaling pathway.1 It primarily acts by counteracting the kinase activity of PI3K, thereby inhibiting the activation of AKT. PTEN may be one of the genetic risk factors for ASD. Mice who have lost PTEN in vivo have a loss of neuronal polarity and neuronal hypertrophy. The TSC1/2 downstream pathway of PI3K/AKT is a candidate for facilitating these cellular changes. In one study which used rapamycin , a mTORC1 inhibitor, to study the TSC/MTORC1 pathway in Pten mutant mice it was found that rapamycin blocks mTORC1 signaling in the CNS. Furthermore, Rapamycin can prevent or reverse macrocephaly in the Pten mutant mice.2 One study estimates a PTEN mutation prevalence of 8.3% in the ASD population. In the study, all patients with PTEN mutations had significant macrocephaly. Some researchers suggest that macrocephaly may be a predisposing a child for autism. 3
References
1. Stiles BL. Phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10: Extending its PTENtacles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;41(4):757-61. PMID 18950730
2. Zhou J et. al. Pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1 suppresses anatomical, cellular, and behavioral abnormalities in neural-specific Pten knock-out mice.J Neurosci. 2009 Feb 11;29(6):1773-83. PMID 19211884
3. Varga EA, et. al. The prevalence of PTEN mutations in a clinical pediatric cohort with autism spectrum disorders, developmental delay, and macrocephaly.Genet Med. 2009 Feb;11(2):111-7. PMID 19265751