Difference between revisions of "CNP RL"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
go back to [[HTAC]] | go back to [[HTAC]] | ||
=== Basic Task Description === | === Basic Task Description === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The CNP "RL" task contains two tasks embedded in one - a probabilistic selection task and a probabilistic reversal learning task. These tasks were designed to assess feedback sensitivity and behavioral flexibility, respectively. Both tasks have been widely used to determine reinforcement learning and behavioral flexibility in healthy and patient populations. The probabilistic selection task, initially designed by Michael Frank, is specifically used to determine participants' tendencies to learn either from positive or negative feedback (e.g., Frank et al., 2004). The probabilistic reversal learning task, originally developed by Trevor Robbins and Robert Rogers (Lawrence et al, 1999; Swainson et al., 2000), examines participants' ability to adapt to changes in learned contingencies. | ||
| − | |||
=== Task Procedure === | === Task Procedure === | ||
Revision as of 23:13, 31 May 2011
go back to HTAC
Contents
Basic Task Description
The CNP "RL" task contains two tasks embedded in one - a probabilistic selection task and a probabilistic reversal learning task. These tasks were designed to assess feedback sensitivity and behavioral flexibility, respectively. Both tasks have been widely used to determine reinforcement learning and behavioral flexibility in healthy and patient populations. The probabilistic selection task, initially designed by Michael Frank, is specifically used to determine participants' tendencies to learn either from positive or negative feedback (e.g., Frank et al., 2004). The probabilistic reversal learning task, originally developed by Trevor Robbins and Robert Rogers (Lawrence et al, 1999; Swainson et al., 2000), examines participants' ability to adapt to changes in learned contingencies.
Task Procedure
For general testing procedure, please refer to LA2K General Testing Procedure [here?].
Task Structure Detail
This is what we had worked on before, but could use updating. We'd like to capture a schema that can handle each of the tasks in the CNP, so please think general when editing -fws
Task Schematic
Schematic of the RL task
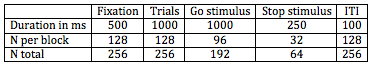
Task Parameters Table
Stimuli
Dependent Variables
The primary dependent variable is ...
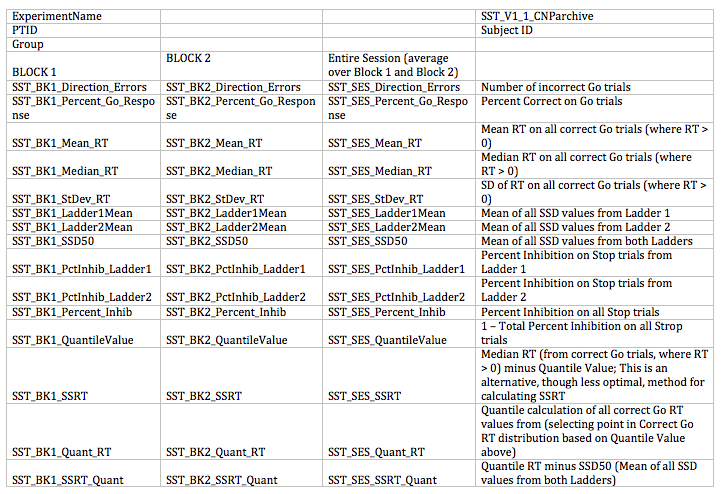
Table of all available variables.
Cleaning Rules
Code/Algorithms
History of Checking Scoring:
Data Distributions
References
Frank MJ, Seeberger LC, O'Reilly RC. By carrot or by stick: cognitive reinforcement learning in Parkinsonism. Science 2004;306:1940-1943
Lawrence AD, Sahakian BJ, Rogers RD, Hodges JR, Robbins TW. Discrimination, reversal, and shift learning in Huntington's disease: mechanisms of impaired response selection. Neuropsychologia 1999;37:1359-1374.
Swainson R, Rogers RD, Sahakian BJ, Summers BA, Polkey CE, Robbins TW. Probabilistic learning and reversal deficits in patients with Parkinson's disease or frontal or temporal lobe lesions: possible adverse effects of dopaminergic medication. Neuropsychologia 2000;38:596-612